Will QLC SSD replace TLC SSD? What is the role of QLC SSD?
With the rise of contemporary applications such as self-media and big data, the need for storage capacity has become increasingly apparent. In the SSD market, the advances in NAND FLASH technology have gradually led to the trend of QLC. The first question that comes to many people's mind is, "Will QLC SSDs gradually replace TLC SSDs?" Today, we're going to examine the role of QLC SSDs in devices based on current trends.
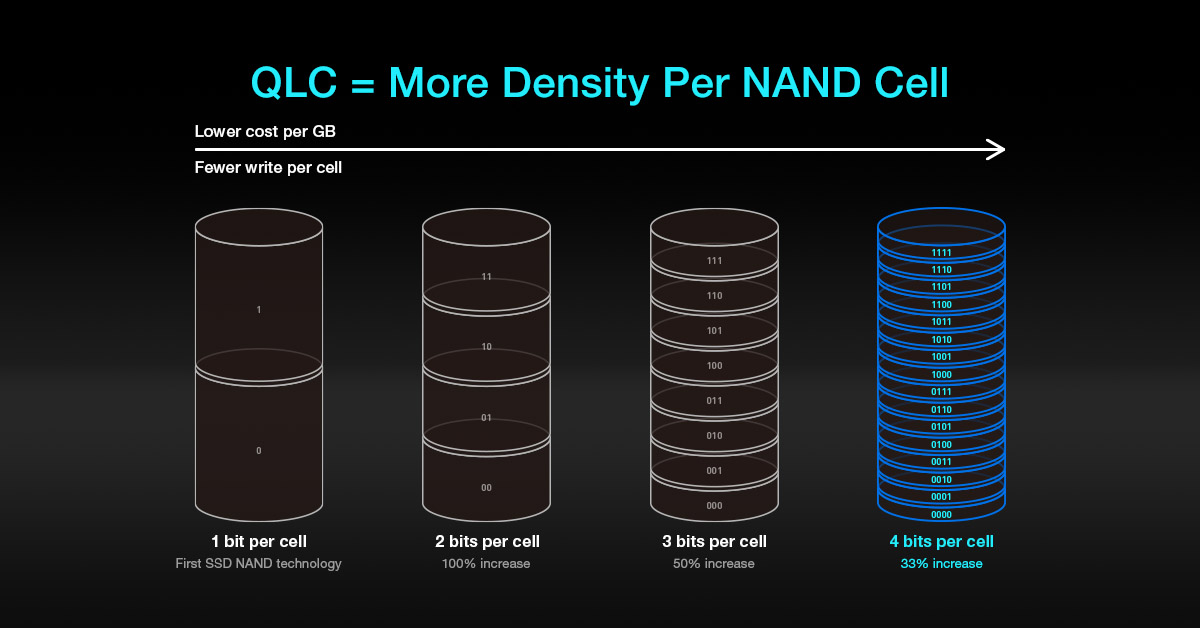
First of all, if you want to resolve your doubt about whether QLC SSDs will gradually replace TLC SSDs, you must first understand the main differences between QLC SSDs and TLC SSDs. I will not provide a detailed explanation here. However, I've include a link to a relevant technical article that we posted before. Please take a look.
For your convenience, here is a brief overview on the major differences.
1、In terms of capacity, QLC can have more capacity in one IC than TLC. If the wafers or ICs are manufactured using QLC technology, they can break through capacity constraints, allowing SSDs to have a bigger capacity boost.
2、In terms of durability, the average write/erase cycles for QLC are about 500 to 1000, while for TLC, it's around 3000. Although there is a significant difference between the two, this feature doesn't affect the average user (non-audio/video creator) too much.
"Capacity" and "durability" are undoubtedly the two most important factors when discussing TLC and QLC SSDs. Firstly, we need to clarify that QLC has the potential to offer higher capacities than TLC SSDs. Therefore, QLC SSDs are designed to popularize high-capacity SSDs such as 1TB or 2TB, making it more likely to replace traditional mechanical hard drives (HDDs). Meanwhile, it also complements TLC SSD. Let' s use the example of a SSD storage solution for desktop computer:
First of all, theoretically, for a desktop computer, SSD storage solutions can be divided into two categories: the system disk and the data disk. Generally, a system disk is used to operate word processing or editing software, which requires a better SSD read/write speed and higher TBW (durability). PCIe M.2 SSDs or 2.5-inch SATA SSDs with good speed specifications are often selected for system disk. On the other hand, a data disk is used purely for storing data. Hence, the larger the capacity of the SSD, the better. These two disks exist for different purposes.
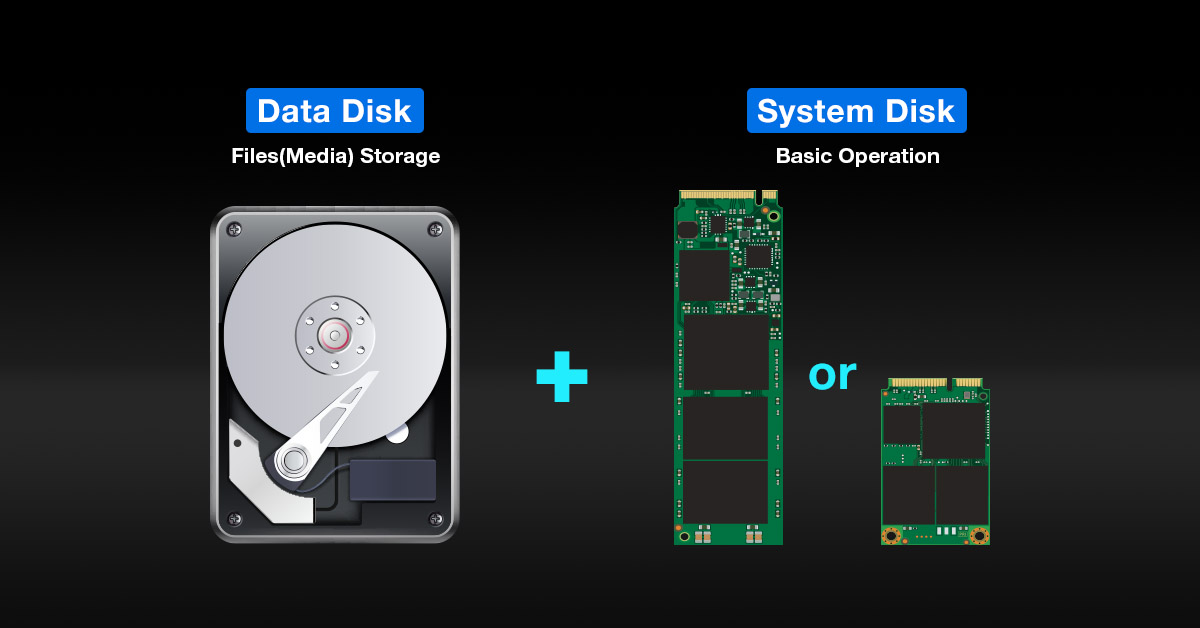
Let's use actual product specifications to find out specifics. We will use the following two products in TEAMGROUP's T-FORCE series: T-FORCE VULCAN Z QLC SSD and T-FORCE VULCAN Z SSD to see how we can achieve an ideal storage solution. First, let's take a look at the specifications.
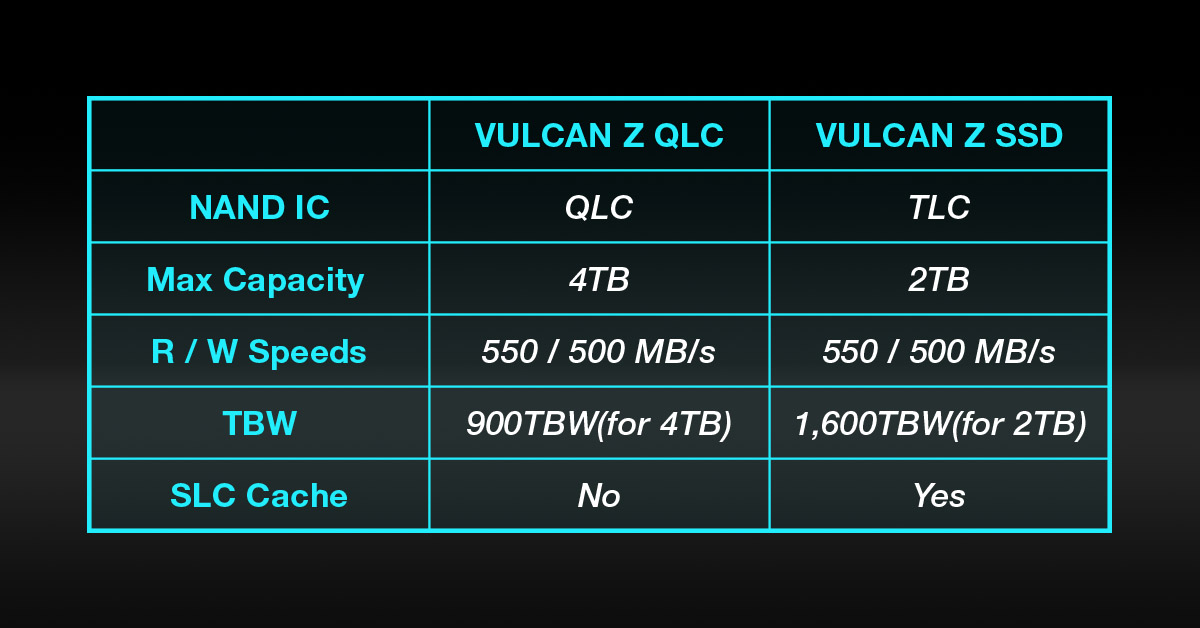
Since a system disk is used to operate word processing or editing software, factors like the R/W speed and TBW (the larger the value, the more durable it is) take on greater importance. VULCAN Z SSD, with its SLC Cache, offer better continuous R/W performance under normal use. Therefore, VULCAN Z SSD will be more suitable as a system disk than VULCAN Z QLC SSD. The VULCAN Z QLC SSD is relatively suitable for use as a data disk. In typical scenarios, when purchasing an SSD on a limited budget, you can get a relatively large capacity at a relatively affordable price by purchasing a QLC SSD over a TLC SSD.
Here you may start to wonder the following: let's buy a M.2 SSD with PCIe interface and high-capacity QLC, which is relatively cheap and offers good performance. It can fulfill all requirements at once! It's important to note that it is not easy to find SSDs with both high R/W speed (PCIe interface) and high capacity (QLC process) with current process technology. Even if SSDs with such specifications do exist, it's not necessarily true that QLC SSDs with the same capacity will cost less than TLC SSDs at this stage.


There are usually differences between personal and enterprise SSDs in terms of the requirements for SSD specification. Both TLC and QLC play their own storage roles depending on the needs of the application. In the near future, QLC may replace most of the TLC. However, theoretically, TLC may not be completely replaced because TLC offers a better TBW than QLC and performs better in terms of durability. This is why SLC SSDs are still in use. Regardless of the NAND FLASH process, demanders will choose according to their different needs. The existence of QLC and TLC SSDs tends to be more complementary than substitutive.
Through this article, we hope you have gained a better understanding of QLC and TLC SSDs. See you next time. Good bye!
RELATED Blog
1
9
11.Jun.2025
Green Tech: Performance Meets Sustainability
05.Mar.2025
Gaming PC vs. Console: Which is Better?
12.Dec.2024
Understanding CAMM2: Is it the End of SO-DIMM?
30.Oct.2024