Understanding USB Flash Drives: Specs and Tips
For students and office workers alike, USB flash drives are indispensable tools. While they might seem straightforward, there's a lot to learn about these handy devices. In this article, I'll break down what you need to know when buying a USB flash drive and share some important do's and don'ts for using them.

Buying a USB flash drive
Most people buy USB flash drives out of necessity—whether for school projects, client presentations on the go, or even for recording driving in an electric vehicle. When choosing one, factors like the material, speed, and storage capacity are key considerations.
Another key point is the type of transmission port your device uses—Type-A or Type-C. Typically, most USB flash drives are either Type-A or dual-port (both Type-A and Type-C), while Type-C-only models are relatively rare. If you frequently switch between your personal laptop and public computers, opting for a dual-port model may be your best bet.
You can also use a Type-A USB stick paired with a Type-A to Type-C adapter, but keep in mind that using an adapter won't boost the drive's speed. This means that the actual transfer speed depends on the drive, the adapter, and the port on your device.
USB Type-A vs. Type-C
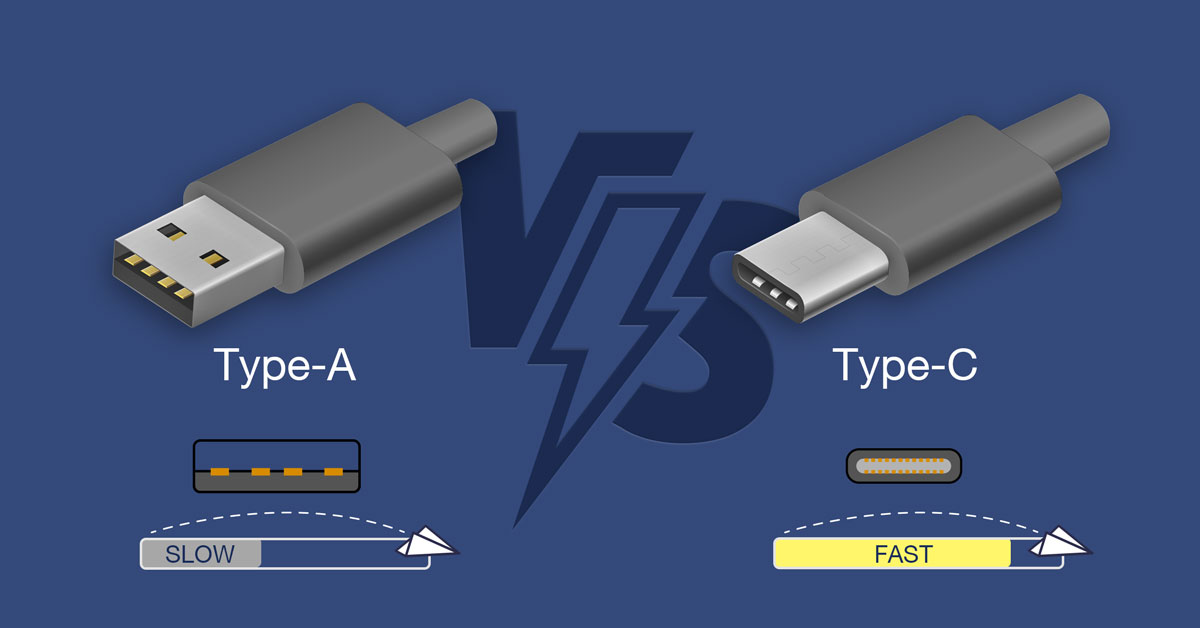
Type-A and Type-C transmission interfaces have distinct characteristics. Visually, the differences are noticeable, with the Type-A port being wider and the Type-C flatter and smaller. Additionally, they also support different maximum speeds: Type-A can handle speeds of up to about 1000 MB/s (or 10 Gbps), whereas Type-C can exceed that. In other words, when considering the theoretical maximum speeds, USB sticks with Type-C ports generally offer higher transfer rates.
However, the data transfer speed you experience will depend on both the USB flash drive and the device it's connected to. For example, laptops may display speed ratings of 10 Gbps or 20 Gbps next to their Type-C ports. This means that even if both ports are Type-C, the actual transfer speed will depend on the maximum speed supported by the device. What's more, if you're using an adapter to convert a Type-A port to Type-C, the adapter's speed capabilities will also impact performance.
In summary, the USB flash drive, the adapter, and the transmission port of the connected device all play crucial roles in determining the final data transfer speed. And that's why it's important to consider the specifications of each device to ensure the best transmission experience.
Using your USB flash drive

When you start using the USB flash drive, you might come across the term "format" in the user manual or in your computer's command window. Formatting can mean two things:
- Partitioning: Dividing the drive into one or more sections to create distinct file systems that facilitate easier data management and access by computers.
- Reorganizing: Completely wiping the drive to start fresh, which may be useful if you suspect file corruption and require the original volume to be recreated.
Next, it's important to understand what a "file system" is. Basically, this is how your drive uniformly manages the file formats in it. Here are the main file formats:
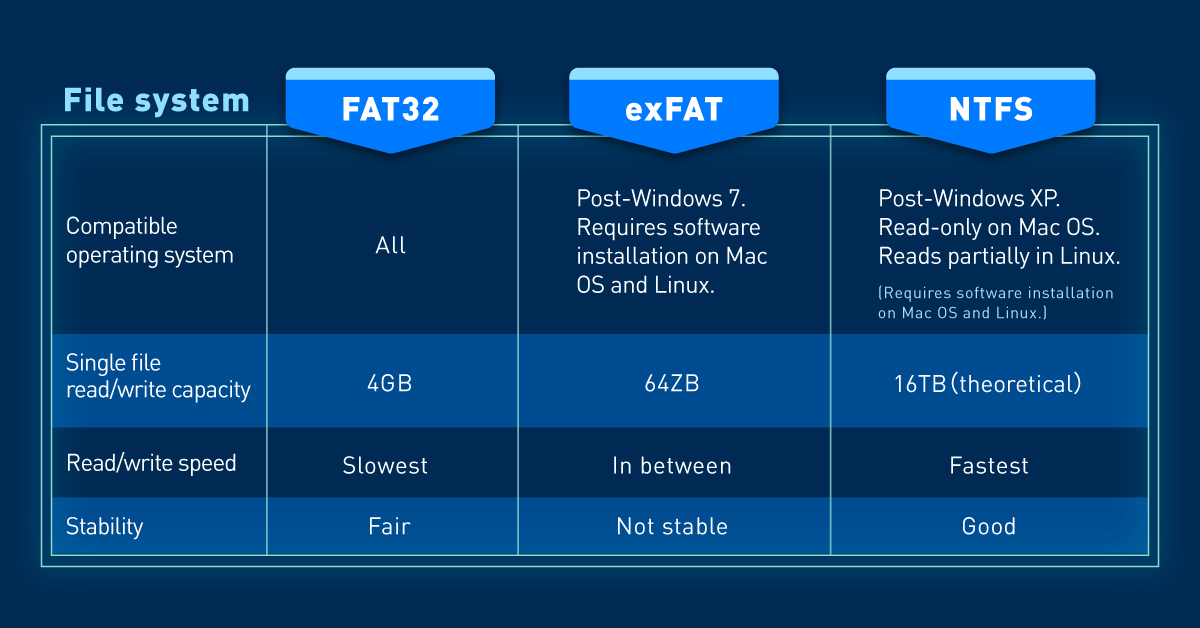
- FAT32: This format is compatible with Mac®, Windows®, and Linux® operating systems, as well as game consoles and most USB-enabled devices, making it a popular choice. However, it has some drawbacks, including limited security and a maximum file size restriction of 4 GB.
- exFAT: Essentially, this file format has no size limit, making it commonly used with most Windows® and Mac® operating systems. That said, if you’re using an older operating system, you may need to update it to properly read and write to hard drives formatted with exFAT.
- NTFS: This is the default format for Microsoft Windows® installations. It supports much larger file sizes, but it is read-only on macOS® X unless you install a third-party NTFS read/write utility.
Here's a quick comparison:
With a better understanding of what formatting entails, you can now categorize it into two distinct types:
- Quick-Level Format: This is the most common process and quickly frees up local hard drive space, typically in under 10 seconds.
- Low-Level Format: More time-consuming, this process completely erases all data from the entire hard drive space.
The only situation that necessitates formatting is when you use a newly purchased USB flash drive that the computer cannot read. In such cases, formatting makes the USB flash drive's file system recognizable. Over time, storage space on a hard drive may become corrupted, and formatting can restore the USB drive to its factory settings and reorganize the storage space. However, this poses a risk of data loss. If you have important files, it's crucial to develop a routine of backing them up regularly. Otherwise, you may find yourself hoping for a miraculous data recovery!
Today, we've covered a range of topics, from selecting a USB flash drive to understanding its usage. We shared insights into specifications and formatting, emphasizing the ongoing advancements in USB flash drive technology. These devices are now available in compact sizes without the need for cables and are often seen as alternatives to portable SSDs. But bear in mind that portable SSDs still outperform USB flash drives in terms of capacity and speed due to more advanced technology. Depending on demand, both options have their dedicated user bases.
TEAMGROUP offers a wide range of USB flash drives designed for various usage scenarios. Here's a helpful guide to assist in finding the USB flash drive that meets your needs and expectations.
See you next time. Bye!
Type-A + Type-C Dual-headed USB flash drive. High-speed model
TEAMGROUP X1 MAX USB 3.2 Gen2 FLASH DRIVE

Type-A + Type-C Dual-headed USB flash drive. Basic model
TEAMGROUP X1 USB 3.2 Gen2 FLASH DRIVE

Electric vehicle application model
TEAMGROUP Model T USB 3.2 Gen1 FLASH DRIVE (BLACK)

Eco-friendly model
TEAMGROUP C175 ECO USB 3.2 Gen1 FLASH DRIVE

High-speed USB Type-A model
TEAMGROUP C212 Extreme Speed USB 3.2 Gen2 FLASH DRIVE

Adapter
TEAMGROUP ON-THE-GO USB 3.2 Type-C to Type-A Female Adapter

RELATED Blog
1
9
11.Jun.2025
Green Tech: Performance Meets Sustainability
05.Mar.2025
Gaming PC vs. Console: Which is Better?
12.Dec.2024