18.May.2024
Understanding the Relationship Between Motherboards and High-Frequency Memory Performance
T-FORCE has rolled out several high-frequency memory models. However, some users can use them without issues while others struggle or can’t get them running at all. Is it just luck? Not always — compatibility with the motherboard may also be a factor in some cases.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Consumer Platforms
- Introduction to HEDT, Workstation, and Server Platforms
- Conclusion
Introduction to Consumer Platforms
The T-FORCE's XTREEM ARGB DDR5, commonly used for U-DIMM memory in consumer platforms like the Intel Z790 or AMD X670E, can handle seriously fast speeds with a maximum specification of 8200 MHz. While the frequencies of newer memories will no doubt get even higher down the road, 8200 MHz is currently pushing the limits of what's achievable.

Reaching this requires a top-tier CPU and motherboard. For Intel Core i9 14900K owners on a budget, pairing the XTREEM ARGB DDR5 with a premium Z790 flagship motherboard from any brand would be a sensible choice to get the most out of both the processor and memory.
Even so, overclocking with high-frequency memory to the extremes can challenge the capabilities of any motherboard – some might have trouble booting or maintaining complete stability under the most taxing workloads.
Not all, not even the priciest flagship motherboards, can handle the fastest memory on the market. A key factor is the number of memory channels on the motherboard, usually limited to two on consumer platforms. This configuration is known as 2DPC (2DIMMs per channel) and is commonly listed on motherboard specs.
These specs also show overclocking limits for different channel modes (1DPC/2DPC) and distinguish between single-sided (1R) and double-sided (2R) particles. However, these limits are often conservative to prioritize stability. After all, the vast majority of computer users (around 95%) do not engage in memory overclocking and simply need their computers to boot up and function reliably.
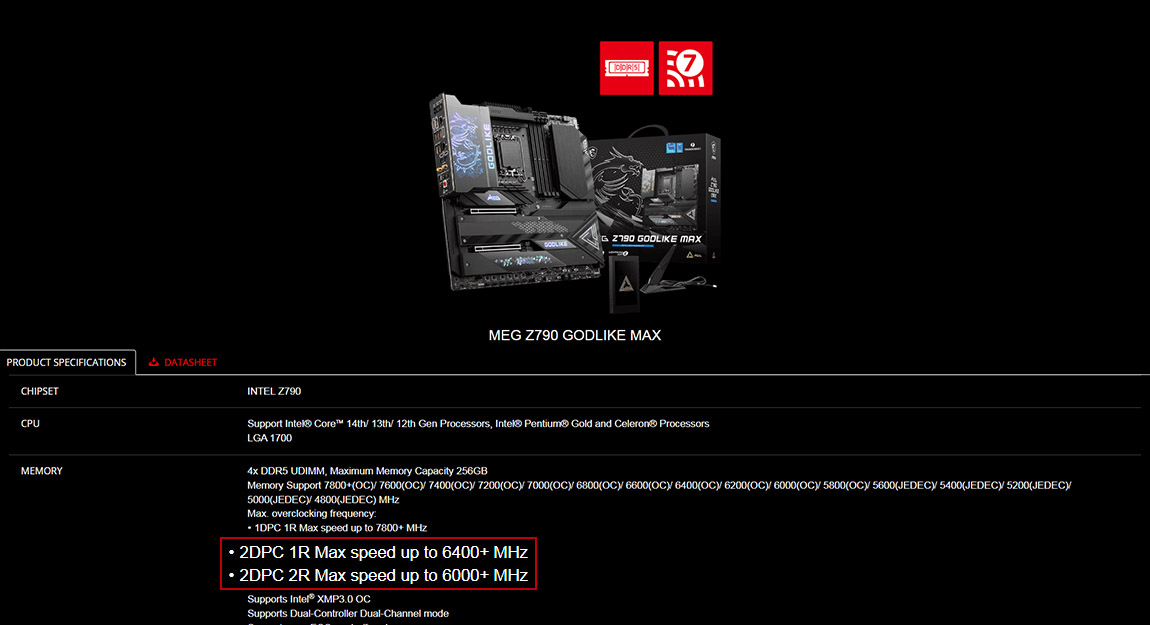
∆ Even the top-tier, flagship MSI MEG Z790 GODLIKE MAX motherboard only lists a maximum speed of 6400+ MHz for 2DPC 1R configurations.
Don't be fooled by the number of memory slots! Dual channel refers to the motherboard’s data transfer pathways, not the slots themselves. Even though a Z790 motherboard might have four DIMM slots, it can still only handle two channels (2DPC) with two DIMMs per channel.
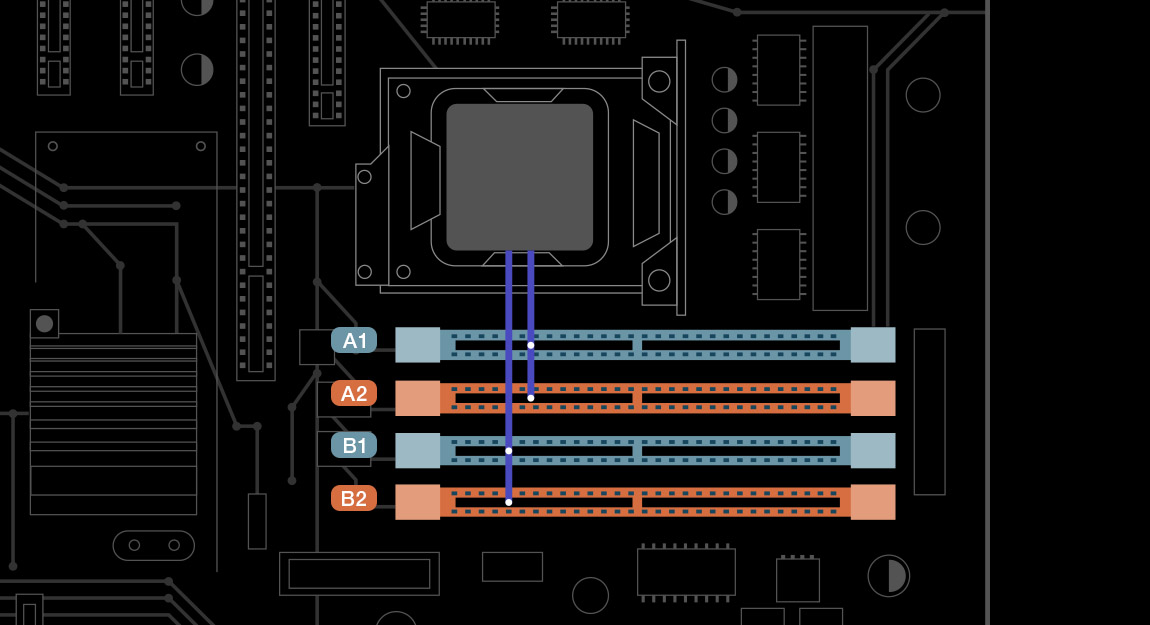
∆ Even though some consumer platforms boast 4 DIMM memory slots, they can only utilize dual-channel memory (2DIMMs per channel), limiting the overall bandwidth.
Introduction to HEDT and Workstation Platforms
While consumer motherboards typically offer dual-channel memory architecture, High-End Desktop (HEDT) and Workstation platforms like AMD WRX90, TRX50, and Intel W790 cater to demanding users by providing more memory channels. These platforms are compatible with T-CREATE MASTER DDR5 R-DIMM memory, optimized for high performance.
Case in point: ASUS W790 motherboards. Both the Pro WS W790-ACE and Pro WS W790E-SAGE SE have 8 x DIMM slots. While the Pro WS W790-ACE uses Quad Channel Memory Architecture, the Pro WS W790E-SAGE SE leverages an even more powerful 8-Channel Memory Architecture.
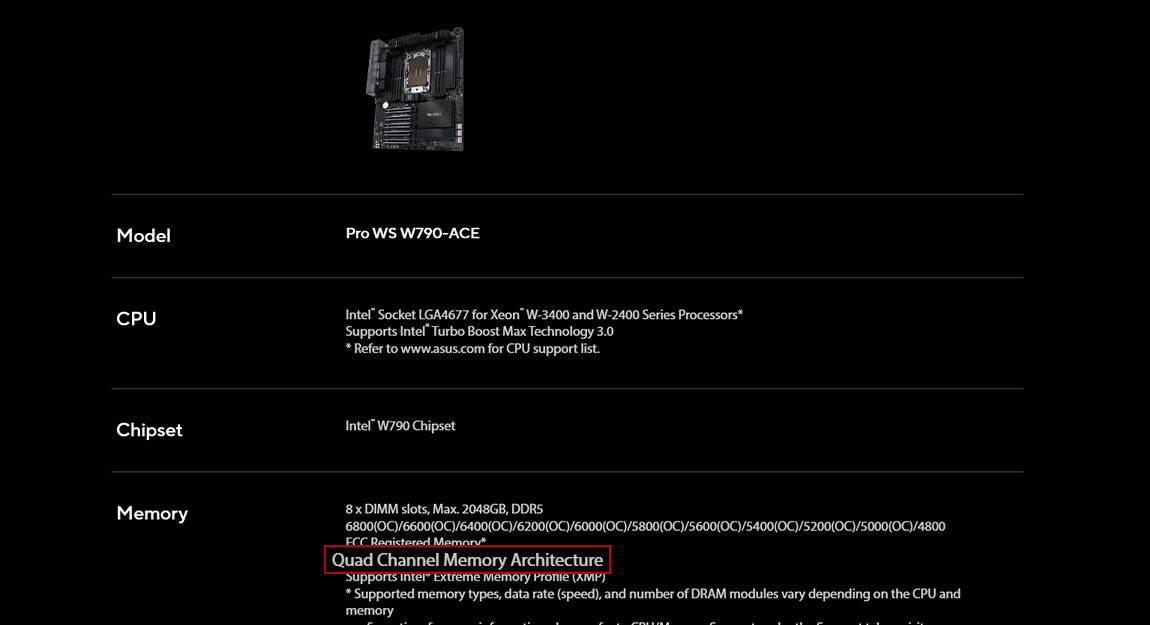
∆ Pro WS W790-ACE uses Quad Channel Memory Architecture.
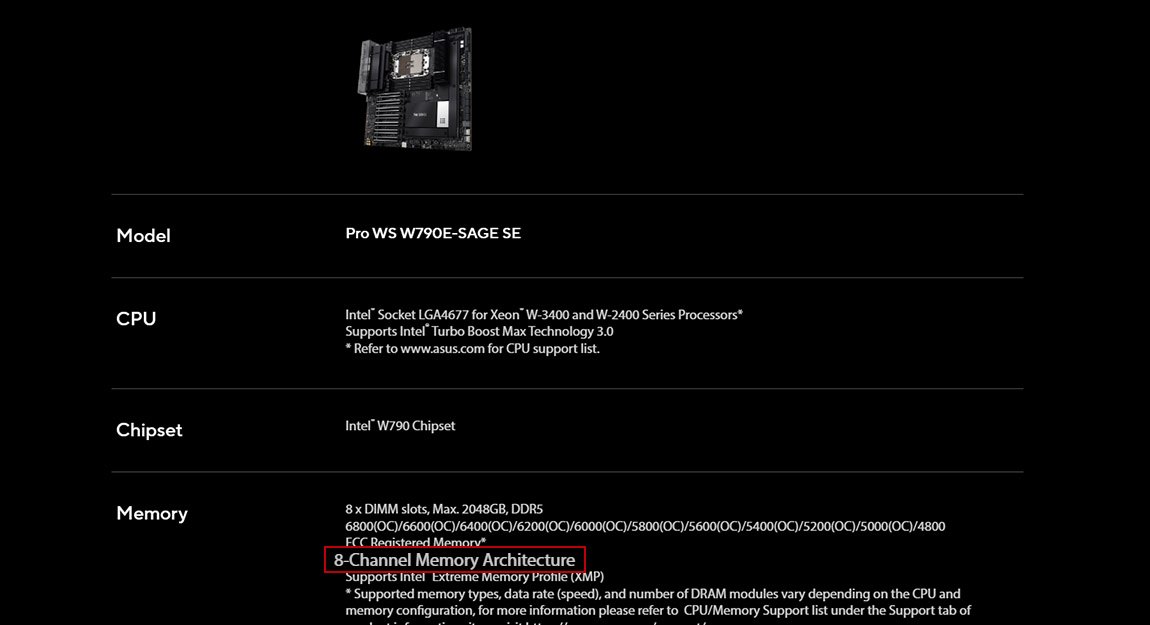
∆ Pro WS W790E-SAGE SE has an 8-Channel Memory Architecture.
Both the Pro WS W790-ACE and Pro WS W790E-SAGE SE offer a whopping eight memory slots. It’s tempting to fill them all with high-performance T-CREATE MASTER DDR5 6800 MHz R-DIMMs! But keep in mind that their memory architecture makes a significant difference in maximizing performance.
The Pro WS W790E-SAGE SE has a powerful eight-channel architecture, where each channel manages a single memory slot. This allows for optimal performance and stability when using all eight R-DIMMs, particularly when pushing memory overclocking.
On the other hand, the Pro WS W790-ACE features a quad-channel architecture. Here, one channel handles two slots. While still capable, this setup might experience slightly lower memory overclocking headroom compared to the 8-channel counterpart.
In short, for users aiming to fully utilize all eight high-frequency R-DIMMs, the Pro WS W790E-SAGE SE with its 8-channel architecture is the better choice for achieving superior memory performance and stability.

∆ This concept of channels and memory slots applies just as well to workstation platforms.
Conclusion

Ensuring stable utilization of high-frequency memory requires a strong team effort. Here’s what matters most:
- CPU’s memory controller (IMC – Integrated Memory Controller): This built-in chip acts like the conductor of the memory orchestra. A powerful IMC is essential for smooth operation.
- BIOS version: While BIOS updates can improve compatibility over time, the design of the motherboard remains fixed, which is what you’re stuck with.
For everyday users on platforms like the Z790 or X670E, the most straightforward approach to harnessing the performance of XTREEM ARGB DDR5 8200 MHz high-frequency memory is to opt for a motherboard with 2 DIMM slots. Examples include the GIGABYTE Z790 AORUS TACHYON X, MSI MEG Z690 UNIFY-X, ROG CROSSHAIR X670E GENE, or some specialized overclocking motherboards offered at competitive prices. Interestingly, even more affordable ITX motherboards often excel in memory overclocking, making it easier to achieve higher frequencies.
While the memory overclocking capabilities of 4DIMM motherboards may not match those of 2DIMM motherboards, they offer the advantage of accommodating larger memory capacities. Moreover, as motherboard brands continue to update and optimize their BIOS versions, compatibility with these faster memory kits will gradually improve. With patience, much of this will unfold over time.

HEDT and Workstation platforms like AMD WRX90, TRX50 or Intel W790 offer a different approach with support for more memory bandwidth channels. The W790 has a twist — while some boast eight memory slots, some models only utilize four memory channels (i.e., only four can work together at maximum efficiency).
Here’s a crucial tip: if you plan to use a large memory kit like a 128 GB (8X16 GB) T-CREATE MASTER DDR5 R-DIMM 6800 MHz, go with W790 models that support eight channels for optimal performance.
RELATED Blog
1
9
11.Jun.2025
Green Tech: Performance Meets Sustainability
05.Mar.2025
Gaming PC vs. Console: Which is Better?
12.Dec.2024
Understanding CAMM2: Is it the End of SO-DIMM?
30.Oct.2024